
NEET Chemistry syllabus 2025 has been revised by the NTA and new practical chemistry topics added and deleted or modified some topics from chemistry syllabus. This blog provides a comprehensive and updated syllabus of chemistry for the NEET 2025 exam. NEET 2025 chemistry syllabus PDF by NTA is also given, students can download it for free.
2 Minutes Read, by Sunil Nain

NEET Chemistry 2025 Syllabus Overview:
Chemistry is not only a scoring subject in the NEET exam but also important for achieving a high overall score in the NEET exam. Chemistry holds significant weightage in the NEET exam, a total of 50 questions are asked in the NEET exam out of which 45 need to be answered making the section 180 marks. Therefore, familiarizing oneself with the NEET chemistry syllabus along with the best books for Chemistry preparation can greatly enhance one's chances of success in this competitive medical entrance examination.
The NEET Chemistry syllabus comprised topics from the class 11 & class 12 chemistry NCERT textbooks and other state board exam books, focussing on fundamental concepts and basic principles of chemistry. It mainly includes three sections namely Physical Chemistry, Inorganic Chemistry & Organic Chemistry. Recently, NTA has updated the chemistry syllabus for NEET 2025 by removing some chapters from the NEET chemistry syllabus and incorporating new practical chemistry topics to ensure a comprehensive assessment of students' knowledge and skills.
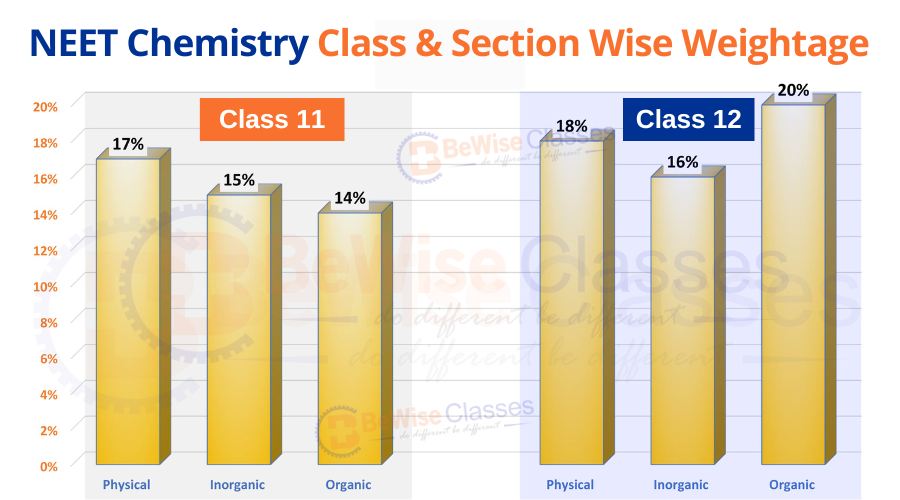
NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2025:
NEET chemistry syllabus covers the important chapters & topics from Physical, Inorganic & organic chemistry sections. Class 11 Chemistry syllabus includes the basic & fundamental topics such as some basic concepts of chemistry, atomic structure, periodic table and chemical bonding etc. Class 12 Chemistry syllabus for NEET 2025 includes advanced topics like important chemical reactions of organic chemistry, chemical kinetics and coordination compounds.
Check NEET 2025 Updated Syllabus Here.
Each topic assesses various skills, including conceptual understanding and practical application, making thorough preparation important for success in the NEET 2025 exam.
NEET 2025 Chemistry Syllabus PDF by NTA:
NTA releases the NEET Chemistry syllabus PDF every year with the information bulletin. The NEET Chemistry syllabus comprehensively details the topics and subtopics slated for inclusion in the upcoming NEET UG exam. This official document works as an indispensable guide for students, offering a well-organized roadmap to streamline their preparation effectively.
Download NEET Chemistry syllabus PDF and refer it to know the updated syllabus so that you don’t miss any important topics or chapter for the NEET 2025 exam. It facilitates effective study planning, enabling you to allocate time strategically based on each section's importance and your level of proficiency.
| Download NEET 2025 Chemistry Syllabus PDF by NTA. |
NEET 2025 Chemistry Syllabus for Class 11:
Class 11 serves as the foundation for the NEET UG exam. The class 11 chemistry syllabus introduces basic and fundamental topics essential for building a strong understanding of chemistry and preparing for the more complex Class 12 topics. Class 11 chemistry syllabus covers chapters such as some basic concepts of chemistry, atomic structure, periodic table, chemical bonding, and thermodynamics.

These topics are relatively easier, allowing students to solve questions easily and achieve a good score in NEET 2025. Therefore, it is essential to have a strong grasp of Class 11 chemistry syllabus by understanding and mastering it effectively. There are 9 chapters in the class 11 chemistry syllabus for the NEET 2025 exam which is given below in the table.
| Chemistry Class 11 Syllabus for NEET 2025 | ||
| S. No | Chapter Name | Sub Topics |
| Chapter 01 | Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | Matter and its nature, Dalton's atomic theory: Concept of atom, molecule, element. and compound. Laws of chemical combination; Atomic and molecular masses, mole concept, molar mass, percentage composition, empirical and molecular formulae: Chemical equations and stoichiometry. |
| Chapter 02 | Atomic Structure |
Nature of electromagnetic radiation, photoelectric effect; Spectrum of the hydrogen atom. Bohr model of a hydrogen atom - its postulates, derivation of the relations for the energy of the electron and radii of the different orbits, limitations of Bohr's model; Dual nature of matter, de Broglie's relationship. Heisenberg uncertainty principle. Elementary ideas of quantum mechanics, quantum mechanics, the quantum mechanical model of the atom, its important features. Concept of atomic orbitals as one-electron wave functions: Variation of Ψ and Ψ 2 with r for 1s and 2s orbitals: various quantum numbers (principal, angular momentum, and magnetic quantum numbers) and their significance; shapes of s, p, and d - orbitals, electron spin and spin quantum number: Rules for filling electrons in orbits - Aufbau principle. Pauli's exclusion principle and Hund's rule, electronic configuration of elements, extra stability of half-filled and completely filled orbitals. |
| Chapter 03 | Classification in Elements and Periodicity in Properties | Modern periodic law and present form of periodic table, s, p, d and f block elements, periodic trends in properties of elements atomic and ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, valence, oxidation states, and chemical reactivity. |
| Chapter 04 | Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure |
Kossel-Lewis approach to chemical bond formation, the concept of ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic Bonding: Formation of ionic bonds, factors affecting the formation of ionic bonds; calculation of lattice enthalpy. Covalent Bonding: Concept of electronegativity. Fajan's rule, dipole moment: Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory and shapes of simple molecules. Quantum mechanical approach to covalent bonding: Valence bond theory - its important features. the concept of hybridization involving s, p, and d orbitals; Resonance. Molecular orbital Theory - Its important features. LCAOs, types of molecular orbitals (bonding, antibonding), sigma and pi-bonds, molecular orbital electronic configurations of homonuclear diatomic molecules, the concept of bond order, bond length, and bond energy. Elementary idea of metallic bonding. Hydrogen bonding and its applications |
| Chapter 05 | Chemical Thermodynamics |
Fundamentals of thermodynamics: System and surroundings, extensive and intensive properties' state functions, types of processes. The first law of thermodynamics - Concept of work, heat internal energy and enthalpy, heat capacity, molar heat capacity; Hess's law of constant heat summation; Enthalpies of bond dissociation, combustion' formation, atomization. sublimation. phase transition, hydration. ionization. and solution. The second law of thermodynamics - Spontaneity of processes: AS of the universe and AC of the system as criteria for spontaneity. Standard Gibbs energy change and equilibrium constant. |
| Chapter 06 | Equilibrium |
Meaning of equilibrium, the concept of dynamic equilibrium. Equilibria involving physical processes: Solid-liquid, liquid - gas and solid-gas equilibria, Henry's law. General characteristics of equilibrium involving physical processes. Equilibrium involving chemical processes: Law of chemical equilibrium, equilibrium constants (Kp and Kc) and their significance, the significance of ΔG and ΔG° in chemical equilibrium, factors affecting equilibrium concentration, pressure, temperature, the effect of catalyst; Le Chatelier's principle. Ionic equilibrium: weak. and strong electrolytes, ionization of electrolytes, various concepts of acids and bases (Arrhenius and Bronsted - Lowry and Lewis) and their ionization, acid-base equilibria (including multistage ionization) and ionization constants, ionization of water. PH scale, common ion effect, hydrolysis of salts and PH of their solutions, the solubility of sparingly soluble salts and solubility products, buffer solutions. |
| Chapter 07 | Redox Reactions | Electronic concepts of oxidation-reduction, redox reactions, oxidation numbers, rules for assigning oxidation numbers, and balancing of redox reactions. |
| Chapter 08 | Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry |
Tetravalency of carbon: Shapes of simple molecules - hybridization (s and p): classification of organic compounds based on functional groups: and those containing halogens, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur; Homologous series: Isomerism - structural and stereoisomerism. Nomenclature (Trivial and IUPAC) Covalent bond fission - Homolytic and heterolytic: free radicals. carbocations. and carbanions: stability of carbocations and free radicals. electrophiles. and nucleophiles. Electronic displacement in a covalent bond: Inductive effect, electromeric effect. resonance and hyperconjugation. Common types of organic reactions- Substitution. addition. elimination, and rearrangement. Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds: Purification - Crystallization. sublimation, distillation, differential extraction, chromatography - principles and their applications. Qualitative analysis - Detection of nitrogen, sulphur, phosphorus and halogens. Quantitative analysis (basic principles only) - Estimation of carbon. hydrogen. nitrogen. halogens. sulphur. phosphorus. Calculations of empirical formulae and molecular formulae: Numerical problems in organic quantitative analysis. |
| Chapter 09 | Hydrocarbons |
Classification, isomerism. IUPAC nomenclature, general methods of preparation, properties, and reactions. Alkanes - Conformations: Sawhorse and Newman projections (of ethane): Mechanism of halogenation of alkanes, projections (of ethane). Alkenes - Geometrical isomerism: Mechanism of electrophilic addition: addition of hydrogen. halogens, water. hydrogen halides (Markownikoffs and peroxide effect): Ozonolysis and polymerization. Alkynes - Acidic character: Addition of hydrogen, halogens, water, and hydrogen halides: Polymerization. Aromatic hydrocarbons - Nomenclature. benzene - structure and aromaticity: Mechanism of substitution: halogenation, nitration. Friedel-Craft's alkylation and acylation, directive influence of the functional group in mono-substituted benzene. |
NEET 2025 Chemistry Syllabus for Class 12:
Class 12 carries more weightage in the NEET exam. Class 12 Chemistry syllabus includes complex and advanced topics such as organic chemistry reactions, chemical kinetics, and electrochemistry.

Understanding these topics thoroughly is essential as it helps in solving high-level questions in the NEET exam effectively. There are 11 chapters in the class 12 chemistry syllabus for the NEET 2025 exam which is given below in the table.
| Chemistry Class 12 Syllabus for NEET 2025 | ||
| S. No | Chapter Name | Sub Topics |
| Chapter 01 | Solutions | Different methods for expressing the concentration of solution - molality, molarity, mole fraction. percentage (by volume and mass both), the vapour pressure of solutions and Raoult's law - Ideal and. non-ideal solutions, vapour pressure - composition, plots for ideal and non-ideal solutions: colligative properties of dilute solutions - a relative lowering of vapour pressure, depression of freezing point, the elevation of.boiling point and osmotic pressure; Determination of molecular mass using colligative properties; Abnormal value of molar mass, Van't Hoff Factor and its significance. |
| Chapter 02 | Electrochemistry |
Electrolytic and metallic conduction, conductance in electrolytic solutions, molar conductivities and their variation with concentration, Kohlrausch's law and its applications. Electrochemical Cells - Electrolytic and Galvanic cells, different types of electrodes, electrode potentials including standard electrode potential, half-cell and cell reactions, emf of a Galvanic cell and its measurement: Nernst equation and its applications; Relationship between cell potential and Gibbs' energy change: Dry cell and lead accumulator; Fuel cells |
| Chapter 03 | Chemical Kinetics | Rate of a chemical reaction, factors affecting the rate of reactions: concentration, temperature, pressure, 'and catalyst; elementary and complex reactions, order and molecularity of reactions, rate law, rate constants and its units, differential and integral forms of zero and first-order reactions, their characteristics and half lives, the effect of temperature on the rate of reactions, Arrhenius theory, activation energy and its calculation, collision theory of bimolecular gaseous reactions (no derivation). |
| Chapter 04 | P-Block Elements | Group 13 to Group 18 Elements General Introduction: Electronic configuration and general trends in physical and chemical properties of elements across the periods and down the groups; unique behaviour of the first element in each group. |
| Chapter 05 | D and F Block Elements |
Transition Elements General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics, general trends in properties, of the first-row transition elements - physical properties, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, atomic radii, colour, catalytic behaviour, magnetic properties, complex formation, interstitial compounds, alloy formation; Preparation, properties and uses of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4. Inner Transition Elements Lanthanoids - Electronic configuration, oxidation states, and lanthanoid contraction. Actinoids - Electronic configuration and oxidation states. |
| Chapter 06 | Co-ordination Compounds | Introduction to coordination compounds. Wener's theory; ligands, coordination number. denticity. chelation; IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds, isomerism: Bonding-Valence bond approach and basic ideas of Crystal field theory, colour and magnetic properties; importance of co-ordination compounds (in qualitative analysis. extraction of metals and in biological systems). |
| Chapter 07 | Halogen Derivatives | General methods of preparation, properties, and reactions; Nature of C-X bond: Mechanisms of substitution reactions. Uses; Environmental effects of chloroform, iodoform freons, and DDT. |
| Chapter 08 | Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers |
Alcohols: Identification of primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols: mechanism of dehydration. Phenols: Acidic nature, electrophilic substitution reactions: halogenation. nitration and sulphonation. Reimer - Tiemann reaction. Ethers: Structure. |
| Chapter 09 | Carbonyl Compounds & Carboxylic Acids |
Aldehyde and Ketones: Nature of carbonyl group; Nucleophilic addition to >C=O group, relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones; Important reactions such as - Nucleophilic addition reactions (addition of HCN. NH3 and its derivatives), Grignard reagent; oxidation: reduction (Wolf Kishner and Clemmensen); the acidity of α-hydrogen. aldol condensation, Cannizzaro reaction. Haloform reaction, Chemical tests to distinguish between aldehydes and Ketones. Carboxylic Acids: Acidic strength and factors affecting it. |
| Chapter 10 | Amines | General methods of preparation. Properties, reactions, and uses. Amines: Nomenclature, classification structure, basic character, and identification of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines and their basic character. Diazonium Salts: Importance in Synthetic Organic Chemistry. |
| Chapter 11 | Biomolecules |
General introduction and importance of biomolecules. CARBOHYDRATES - classification; aldoses and ketoses: monosaccharides (glucose and fructose) and constituent monosaccharides of oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, and maltose) PROTEINS.Elementary Idea of α-amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides.Proteins: primary. secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins enzymes. VITAMINS - Classification and functions NUCLEIC ACIDS - Chemical constitution of DNA and RNA Biological functions of nucleic acids Hormones (General Introduction) |
| Chapter 12 | Principles Related to Practical Chemistry |
|
Section Wise Chemistry Syllabus for NEET 2025:
NEET Chemistry syllabus comprises three sections namely Physical, Inorganic & Organic Chemistry. Each section covers specific topics which check the different skills of students in the NEET exam. Understanding these three sections is crucial for comprehensive preparation and success in the NEET exam.
Physical Chemistry Syllabus for NEET 2025:
Physical Chemistry section deals with concepts such as mole concept, atomic structure thermodynamics, chemical equilibrium, and redox reactions. It focuses on the principles and theories that control chemical processes and reactions. Physical chemistry carries more weightage in the NEET UG exam. 18-20 questions out of 50 questions are asked from physical chemistry in the NEET exam. Understanding and mastering this section is essential to score well in chemistry in the NEET exam.
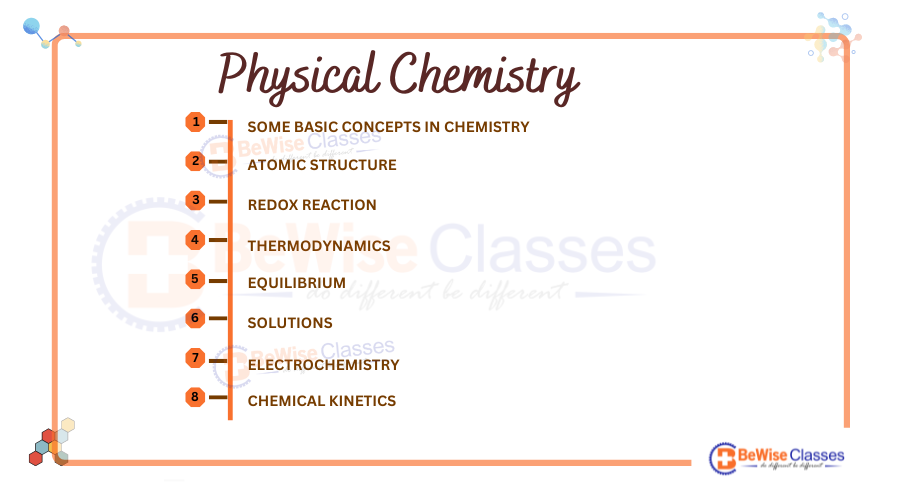
Unit I: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Matter and its nature, Dalton's atomic theory: Concept of atom, molecule, element. and compound. Laws of chemical combination; Atomic and molecular masses, mole concept, molar mass, percentage composition, empirical and molecular formulae: Chemical equations and stoichiometry.
Unit II: Atomic Structure
Nature of electromagnetic radiation, photoelectric effect; Spectrum of the hydrogen atom. Bohr model of a hydrogen atom - its postulates, derivation of the relations for the energy of the electron and radii of the different orbits, limitations of Bohr's model; Dual nature of matter, de Broglie's relationship.
Heisenberg uncertainty principle. Elementary ideas of quantum mechanics, quantum mechanics, the quantum mechanical model of the atom, its important features. Concept of atomic orbitals as one-electron wave functions: Variation of Ψ and Ψ 2 with r for 1s and 2s orbitals: various quantum numbers (principal, angular momentum, and magnetic quantum numbers) and their significance;
shapes of s, p, and d - orbitals, electron spin and spin quantum number: Rules for filling electrons in orbits - Aufbau principle. Pauli's exclusion principle and Hund's rule, electronic configuration of elements, extra stability of half-filled and completely filled orbitals.
Unit III: Chemical Thermodynamics
Fundamentals of thermodynamics: System and surroundings, extensive and intensive properties' state functions, types of processes. The first law of thermodynamics - Concept of work, heat internal energy and enthalpy, heat capacity, molar heat capacity; Hess's law of constant heat summation; Enthalpies of bond dissociation, combustion' formation, atomization. sublimation. phase transition, hydration. ionization. and solution.
The second law of thermodynamics - Spontaneity of processes: AS of the universe and AC of the system as criteria for spontaneity. Standard Gibbs energy change and equilibrium constant.
Unit IV: Equilibrium
Meaning of equilibrium, the concept of dynamic equilibrium. Equilibria involving physical processes: Solid-liquid, liquid - gas and solid-gas equilibria, Henry's law. General characteristics of equilibrium involving physical processes.
Equilibrium involving chemical processes: Law of chemical equilibrium, equilibrium constants (Kp and Kc) and their significance, the significance of ΔG and ΔG° in chemical equilibrium, factors affecting equilibrium concentration, pressure, temperature, the effect of catalyst; Le Chatelier's principle.
Ionic equilibrium: weak. and strong electrolytes, ionization of electrolytes, various concepts of acids and bases (Arrhenius and Bronsted - Lowry and Lewis) and their ionization, acid-base equilibria (including multistage ionization) and ionization constants, ionization of water. PH scale, common ion effect, hydrolysis of salts and PH of their solutions, the solubility of sparingly soluble salts and solubility products, buffer solutions.
Unit V: Redox Reactions
Electronic concepts of oxidation-reduction, redox reactions, oxidation numbers, rules for assigning oxidation numbers, and balancing of redox reactions.
Unit VI: Solutions
Different methods for expressing the concentration of solution - molality, molarity, mole fraction. percentage (by volume and mass both), the vapour pressure of solutions and Raoult's law - Ideal and. non-ideal solutions, vapour pressure - composition, plots for ideal and non-ideal solutions: colligative properties of dilute solutions - a relative lowering of vapour pressure, depression of freezing point, the elevation of.boiling point and osmotic pressure; Determination of molecular mass using colligative properties; Abnormal value of molar mass, Van't Hoff Factor and its significance.
Unit VII: Electrochemistry
Electrolytic and metallic conduction, conductance in electrolytic solutions, molar conductivities and their variation with concentration, Kohlrausch's law and its applications. Electrochemical Cells - Electrolytic and Galvanic cells, different types of electrodes, electrode potentials including standard electrode potential, half-cell and cell reactions, emf of a Galvanic cell and its measurement: Nernst equation and its applications; Relationship between cell potential and Gibbs' energy change: Dry cell and lead accumulator; Fuel cells.
Unit VIII: Chemical Kinetics
Rate of a chemical reaction, factors affecting the rate of reactions: concentration, temperature, pressure, 'and catalyst; elementary and complex reactions, order and molecularity of reactions, rate law, rate constants and its units, differential and integral forms of zero and first-order reactions, their characteristics and half lives, the effect of temperature on the rate of reactions, Arrhenius theory, activation energy and its calculation, collision theory of bimolecular gaseous reactions (no derivation).
Inorganic Chemistry Syllabus for NEET 2025:
Inorganic chemistry deals with the properties, structures, and reactions of inorganic compounds and periodic trends. Topics include the periodic table, coordination compounds, and chemical bonding in inorganic molecules. Without understanding, inorganic chemistry, it is very difficult to have a good command of chemistry.
Every NEET aspirant must have a good grasp of inorganic chemistry. 13-15 questions are asked from the inorganic chemistry section in the NEET UG exam.
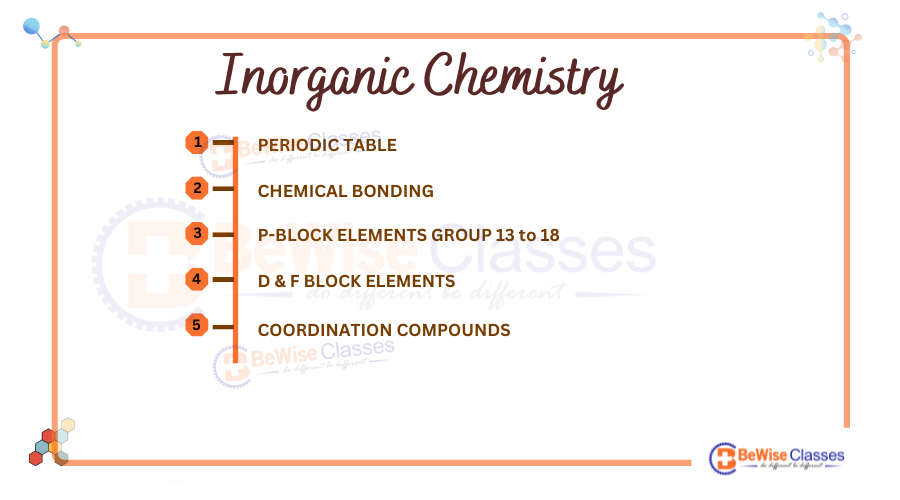
Unit I: Classification in Elements and Periodicity in Properties
Modern periodic law and present form of periodic table, s, p, d and f block elements, periodic trends in properties of elements atomic and ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, valence, oxidation states, and chemical reactivity.
Unit II: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Kossel-Lewis approach to chemical bond formation, the concept of ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic Bonding: Formation of ionic bonds, factors affecting the formation of ionic bonds; calculation of lattice enthalpy.
Covalent Bonding: Concept of electronegativity. Fajan's rule, dipole moment: Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory and shapes of simple molecules. Quantum mechanical approach to covalent bonding: Valence bond theory - its important features. the concept of hybridization involving s, p, and d orbitals; Resonance.
Molecular orbital Theory - Its important features. LCAOs, types of molecular orbitals (bonding, antibonding), sigma and pi-bonds, molecular orbital electronic configurations of homonuclear diatomic molecules, the concept of bond order, bond length, and bond energy. Elementary idea of metallic bonding. Hydrogen bonding and its applications.
Unit III: P-Block Elements
Group 13 to Group 18 Elements General Introduction: Electronic configuration and general trends in physical and chemical properties of elements across the periods and down the groups; unique behaviour of the first element in each group.
Unit IV: D and F Block Elements
Transition Elements General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics, general trends in properties, of the first-row transition elements - physical properties, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, atomic radii, colour, catalytic behaviour, magnetic properties, complex formation, interstitial compounds, alloy formation; Preparation, properties and uses of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4. Inner Transition Elements
Lanthanoids - Electronic configuration, oxidation states, and lanthanoid contraction.
Actinoids - Electronic configuration and oxidation states.
Unit V: Co-ordination Compounds
Introduction to coordination compounds. Wener's theory; ligands, coordination number. denticity. chelation; IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds, isomerism: Bonding-Valence bond approach and basic ideas of Crystal field theory, colour and magnetic properties; importance of co-ordination compounds (in qualitative analysis. extraction of metals and in biological systems).
Organic Chemistry Syllabus for NEET 2025:
This section covers the structure, properties, reactions, and synthesis of organic compounds and the mechanism of reactions. It includes topics such as hydrocarbons, organic compounds containing halogens, oxygen, nitrogen, and polymers.
Organic chemistry section is not only a scoring section but it also saves a lot of time during the exam. If a student has a good understanding of organic chemistry topics, he can solve questions in seconds and it helps to score maximum in chemistry in the NEET UG exam. 18-20 questions are asked from the organic chemistry in the NEET UG exam.
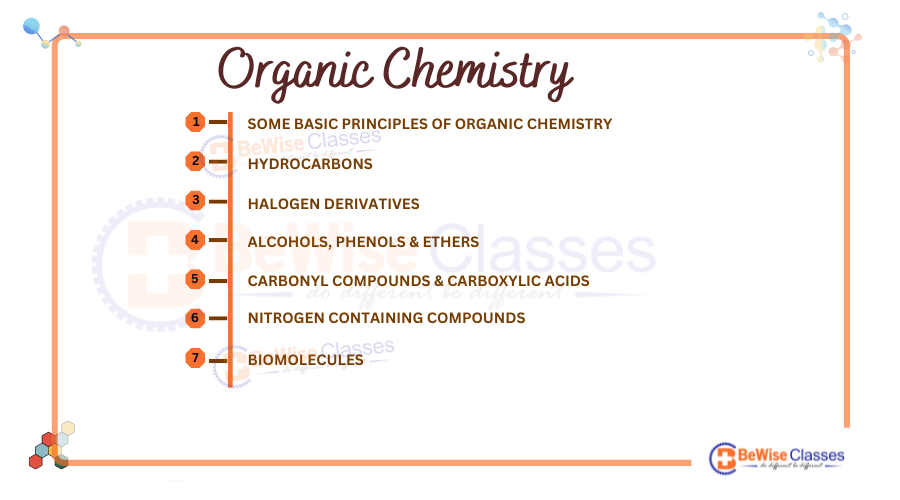
Unit I: Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
Tetravalency of carbon: Shapes of simple molecules - hybridization (s and p): crassification of organic compounds based on functional groups: and those containing halogens, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur; Homologous series:
Isomerism - structural and stereoisomerism.
Nomenclature (Trivial and IUPAC)
Covalent bond fission - Homolytic and heterolytic: free radicals. carbocations. and carbanions: stability of carbocations and free radicals. electrophiles. and nucleophiles. Electronic displacement in a covalent bond Inductive effect, electromeric effect. resonance and hyperconjugation.
Common types of organic reactions- Substitution. addition. elimination, and rearrangement.
Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds Purification - Crystallization. sublimation, distillation, differential extraction, chromatography - principles and their applications. Qualitative analysis - Detection of nitrogen, sulphur, phosphorus and halogens. Quantitative analysis (basic principles only) - Estimation of carbon. hydrogen. nitrogen. halogens. sulphur. phosphorus. Calculations of empirical formulae and molecular formulae: Numerical problems in organic quantitative analysis.
Unit II: Hydrocarbons
Classification, isomerism. IUPAC nomenclature, general methods of preparation, properties, and reactions.
Alkanes - Conformations: Sawhorse and Newman projections (of ethane): Mechanism of halogenation of alkanes, projections (of ethane).
Alkenes - Geometrical isomerism: Mechanism of electrophilic addition: addition of hydrogen. halogens, water. hydrogen halides (Markownikoffs and peroxide effect): Ozonolysis and polymerization.
Alkynes - Acidic character: Addition of hydrogen, halogens, water, and hydrogen halides: Polymerization.
Aromatic hydrocarbons - Nomenclature. benzene - structure and aromaticity: Mechanism of substitution: halogenation, nitration. Friedel-Craft's alkylation and acylation, directive influence of the functional group in mono-substituted benzene.
Unit III: Organic Compounds Containing Halogen
General methods of preparation, properties, and reactions; Nature of C-X bond: Mechanisms of substitution reactions. Uses; Environmental effects of chloroform, iodoform freons, and DDT.
Unit IV: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers
General methods of preparation, properties, reactions, and uses.
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Alcohols: Identification of primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols: mechanism of dehydration.
Phenols: Acidic nature, electrophilic substitution reactions: halogenation. nitration and sulphonation. Reimer - Tiemann reaction. Ethers: Structure.
Unit V: Carbonyl Compounds & Carboxylic Acids:
Aldehyde and Ketones: Nature of carbonyl group; Nucleophilic addition to >C=O group, relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones; Important reactions such as - Nucleophilic addition reactions (addition of HCN. NH3 and its derivatives), Grignard reagent; oxidation: reduction (Wolf Kishner and Clemmensen); the acidity of α-hydrogen. aldol condensation, Cannizzaro reaction. Haloform reaction, Chemical tests to distinguish between aldehydes and Ketones.
Carboxylic Acids Acidic strength and factors affecting it.
Unit VI: Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
General methods of preparation. Properties, reactions, and uses. Amines: Nomenclature, classification structure, basic character, and identification of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines and their basic character. Diazonium Salts: Importance in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.
Unit VII: Biomolecules
General introduction and importance of biomolecules.
CARBOHYDRATES - classification; aldoses and ketoses: monosaccharides (glucose and fructose) and constituent monosaccharides of oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, and maltose)
PROTEINS - Elementary Idea of α-amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides.Proteins: primary. secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins enzymes.
VITAMINS - Classification and functions
NUCLEIC ACIDS - Chemical constitution of DNA and RNA Biological functions of nucleic acids Hormones (General Introduction)
Practical Chemistry Syllabus for NEET 2025:
Recently revised by NTA, the NEET Chemistry syllabus includes additional topics beyond those covered in NCERT Chemistry textbooks, therefore aspirants are required to pay keen attention. It incorporates experimental-based topics in chemistry focusing on the identification of functional groups like hydroxyl and carbonyl, as well as inorganic compounds such as Mohr’s salt and potash alum. 4-5 questions based on practical chemistry topics were asked in the NEET 2024 exam. If a student wants to score 180 out of 180 marks in chemistry, he must cover these topics thoroughly.
Principles Related to Practical Chemistry:
Mastering the NEET Chemistry 2025 syllabus is crucial for aspirants aiming to excel in this competitive medical entrance examination. With Chemistry holding substantial weightage, comprising 50 questions and totaling 180 marks, familiarity with the syllabus is key to achieving a high overall score. The updated syllabus, which integrates new practical chemistry topics while retaining core concepts from class 11 and 12 NCERT textbooks, underscores the importance of a comprehensive understanding.
Candidates must prioritize thorough preparation across Physical, Inorganic, and Organic Chemistry sections, leveraging resources that align with the updated syllabus. This approach ensures they are well-equipped to tackle the diverse range of topics and question types expected in the NEET 2025 exam. By focusing on both conceptual understanding and practical application, aspirants can enhance their readiness and maximize their chances of success on exam day.
Also Read: